· physical Media:
·
· Twisted pair - Wire twisted to avoid crosstalk interference. It may be shielded or unshielded.
· UTP-Unshielded Twisted Pair. Normally UTP contains 8 wires or 4 pair. 100 meter maximum length. 4-100 Mbps speed.
· STP-Shielded twisted pair. 100 meter maximum length. 16-155 Mbps speed. Lower electrical interference than UTP.
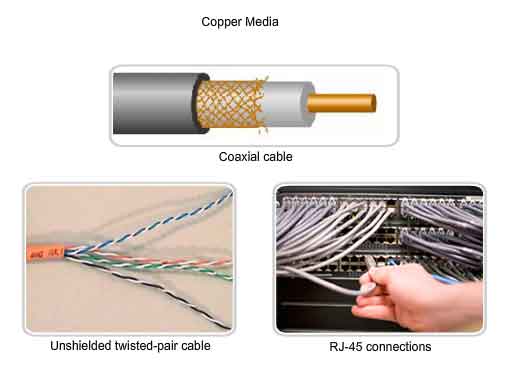
· Coaxial - Two conductors separated by insulation such as TV 75 ohm cable. Maximum length of 185 to 500 meters.
· Thinnet - Thinnet uses a British Naval Connector (BNC) on each end. Thinnet is part of the RG-58 family of cable*. Maximum cable length is 185 meters. Transmission speed is 10Mbps. Thinnet cable should have 50 ohms impedance and its terminator has 50 ohms impedance. A T or barrel connector will have no impedance. Maximum thinnet nodes are 30 on a segment. One end of each cable is grounded.
· Thicknet - Half inch rigid cable. Maximum cable length is 500 meters. Transmission speed is 10Mbps. Expensive and is not commonly used. (RG-11 or RG-8). A vampire tap or piercing tap is used with a transceiver attached to connect computers to the cable. 100 connections may be made. The computer has an attachment unit interface (AUI) on its network card which is a 15 pin DB-15 connector. The computer is connected to the transceiver at the cable from its AUI on its network card using a drop cable. Maximum thicknet nodes are 100 on a segment. One end of each cable is grounded.
· The RG value for cable types refers to its size. Coax cable types:
· RG-58 /U - 50 ohm, with a solid copper wire core for thin ethernet.
· RG-58 A/U* - 50 ohm, with a stranded wire core.
· RG-58 C/U* - Military version of RG-58 A/U.
· RG-59 - 75 ohm, for broadband transmission such as cable TV.
· RG-62 - 93 ohm, primarily used for ArcNet.
· RG-6 - Used for satellite cable (if you want to run a cable to a satellite!).
· RG-8 - 50 ohm thick ethernet.
· RG-11 - 75 ohm thick ethernet.
· *Only these are part of the IEEE specification for ethernet networks.
· Fiber-optic - Data is transmitted using light rather than electrons. Usually there are two fibers, one for each direction. Cable length of 2 Kilometers. Speed from 100Mbps to 2Gbps. This is the most expensive and most difficult to install, but is not subject to interference. Two types of cables are:
· Single mode cables for use with lasers has greater bandwidth and costs more. Injection laser diodes (ILD) work with single mode cable.
· Multimode cables for use with Light Emitting Diode (LED) drivers. All signals appear to arrive at the same time. P intrinsic N diodes or photodiodes are used to convert light to electric signals when using multimode.

Wireless Media
Transmission of waves take place in the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The carrier frequency of the data is expressed in cycles per second called hertz(Hz). Low frequency signals can travel for long distances through many obstacles but can not carry a high bandwidth of date while high frequency signals can travel for shorter distances through few obstacles and carry a narrow bandwidth. Also the noise effect on the signal is inversely proportional to the power of the radio transmitter. The three broad categories of wireless media are:
Radio - 10 Khz to 1 Ghz. It is broken into many bands including AM, FM, and VHF bands. The Federal communications Commission (FCC) regulates the assignment of these frequencies. Frequencies for unregulated use are:
902-928Mhz - Cordless phones, remote controls.
2.4 Ghz
5.72-5.85 Ghz
Microwave
Terrestrial - Used to link networks over long distances but the two microwave towers must have a line of sight between them. The frequency is usually 4-6GHz or 21-23GHz. Speed is often 1-10Mbps. The signal is normally encrypted for privacy. Two nodes may exist.
Satellite - A satellite orbits at 22,300 miles above the earth which is an altitude that will cause it to stay in a fixed position relative to the rotation of the earth. This is called a geosynchronous orbit. A station on the ground will send and receive signals from the satellite. The signal can have propagation delays between 0.5 to 5 seconds due to the distances involved. The transmission frequency is normally 11-14GHz with a transmission speed in the range of 1-10Mbps.
Infared - Infared is just below the visible range of light between 100Ghz and 1000Thz. A light emitting diode (LED) or laser is used to transmit the signal. The signal cannot travel through objects. Light may interfere with the signal. The types of infared are
Point to point - Transmission frequencies are 100GHz-1,000THz . Transmission is between two points and is limited to line of sight range. It is difficult to eavesdrop on the transmission. The speed is 100Kbps to 16Mbps
broadcast - The signal is dispersed so several units may receive the signal. The unit used to disperse the signal may be reflective material or a transmitter that amplifies and retransmits the signal. Normally the speed is limited to 1Mbps. The transmission frequency is normally 100GHz-1,000THz with transmission distance in 10's of meters. Installation is easy and cost is relatively inexpensive for wireless.
Terms:
wireless bridge - Microwave or infared is used between two line of site points where it is difficult to run wire.
CDPD - Cellular Digital Packet Data will allow network connections for mobile users using satellites.


No comments:
Post a Comment