Special folder: On Microsoft Windows, a special folder is a folder which is presented to the user through an interface as an abstract concept, instead of an absolute folder path. This makes it possible for an application to ask the operating system where an appropriate location for certain kinds of files can be found, regardless of what version or language of operating system is being used. Windows uses the concept of special folders to present the contents of the storage devices connected to the computer in a fairly consistent way that frees the user from having to deal with absolute file paths, which can (and often do) change between operating system versions, and even individual installations. The idea has evolved over time, with new special folders being added in every version of Windows since their introduction in Windows 95.
Microsoft's "Designed for Windows" logo requirements[1][not in citation given] state that an application must make use of special folders locations to locate the appropriate folders in which documents and application settings should be stored.
A special folder can either be a reference to a physical file system directory, or a reference to a "virtual" folder. In the former case, they are analogous to environment variables — in fact, many of the environment variables that are set in a user's session are defined by where the special folders are set to point to.
Virtual folders, however, do not actually exist on the file system; they are instead presented through Windows Explorer as a tree of folders that the user can navigate. This is known as the Shell namespace. On Windows XP systems, the root of this namespace is the Desktop virtual folder, which contains the My Documents, My Computer, My Network Places (Network Neighborhood in Windows 95 and 98) and Recycle Bin virtual folders. Some virtual folders (like Desktop) have an accompanying special folder that is a reference to a directory on the physical file system. Windows Explorer displays the combined contents of a virtual folder and its associated file system folder to the user. This can be seen in Figure 1, which shows the Folder view in Windows XP's Explorer; in the Desktop virtual folder, the four standard virtual folders can be seen, as well as an additional folder, "a folder on the desktop", which is a real folder located in the Desktop directory in the user's profile.
Some third-party programs add their own virtual folders to Windows Explorer.
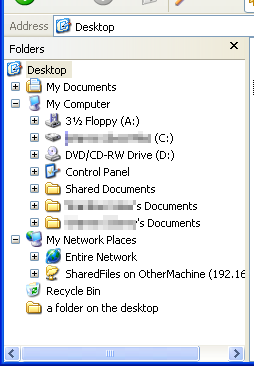
Windows special folder: IT has Desktop folder, Start menu folder & personal documents folder. the special folder name is used to index into the collection to retrive the special folder we want.
Virtual special folders; 1. Recycle bin.
2. Control panel.
3. Desktop.
4. internet.
5. My documents
6. Network.
7. Search result & printers.
* Disk cleaner ::Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe) is a computer maintenance utility included in Microsoft Windowsdesigned to free up disk space on a computer's hard drive. The utility first searches and analyzes the hard drive for files that are no longer of any use, and then removes the unnecessary files. There are a number of different file categories that Disk Cleanup targets when performing the initial disk analysis:
Compression of old files
Temporary Internet files
Temporary Windows file
Downloaded Program files
Recycle Bin
Removal of unused applications or optional Windows components
Setup Log files
Offline files
The above list, however, is not exhaustive. For instance, 'Temporary Remote Desktop files' and 'Temporary Sync Files' may appear only under certain computer configurations, differences such as Windows Operating System and use of additional programs such as Remote Desktop. The option of removal hibernation data may not be ideal for some users as this may remove the hibernate option.
Aside from removing unnecessary files, users also have the option of compressing files that have not been accessed over a set period of time. This option provides a systematic compression scheme. Infrequently accessed files are compressed to free up disk space while leaving the frequently used files uncompressed for faster read/write access times. If after file compression, a user wishes to access a compressed file, the access times may be increased and vary from system to system. In addition to the categories that appear on the Disk Cleanup tab, the More Options tab offers additional options for freeing up hard drive space through removal of optional Windows components, installed programs, and all but the most recent System Restore point or Shadow Copy data in some versions of Microsoft Windows.
Disk Defragmenter:Disk Defragmenter is a utility in Microsoft Windows designed to increase access speed by rearranging filesstored on a disk to occupy contiguous storage locations, a technique called defragmentation. Defragmenting a disk minimizes head travel, which reduces the time it takes to read files from and write files to the disk.[1]Beginning with Windows XP, Disk Defragmenter also reduces system startup times.
system restore:System Restore is a component of Microsoft's Windows Me, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7, but not Windows 2000,[1] operating systems that allows for the rolling back of system files, registry keys, installed programs, etc., to a previous state in the event of system malfunction or failure.
The Windows Server operating system family does not include System Restore. The System Restore built into Windows XP can be installed on a Windows Server 2003 machine,[2] although this is not supported by Microsoft.
In Windows Vista and later versions, System Restore has an improved interface and is based on Shadow Copy technology. In prior Windows versions it was based on a file filter that watched changes for a certain set of file extensions, and then copied files before they were overwritten.[3] Shadow Copy has the advantage that block-level changes in files located in any directory on the volume can be monitored and backed up regardless of their location.

No comments:
Post a Comment